British Heritage
Remember, Cherish, Learn.
beta
Time - Greenwich Mean Time, now UTC
The Legacy of Greenwich Mean Time in British Heritage.
The ability to accurately measure time is a fundamental aspect of modern life, affecting nearly everything from navigation and computing to scheduling and scientific study. The development and implementation of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as a standardised timekeeping method represents a crucial contribution to British heritage and global society as a whole. Its evolution into Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and its ongoing relevance emphasise the significant role Britain played in establishing this foundational timekeeping system.
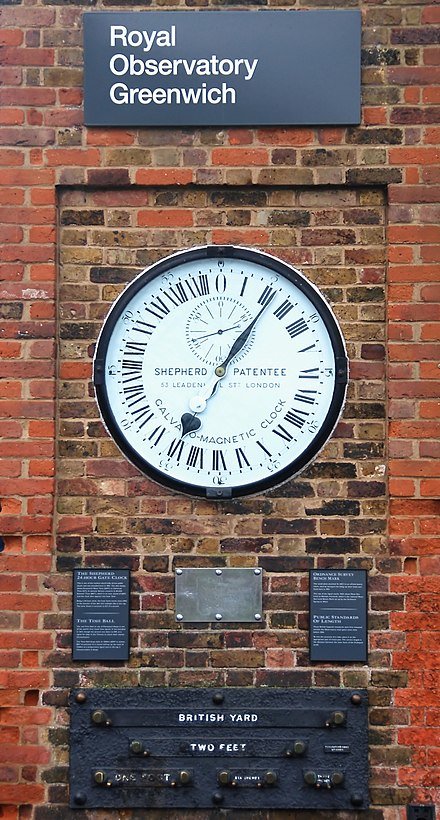
The emergence of GMT can be traced back to 1884 at the Greenwich Observatory in the United Kingdom. Prior to this, towns and cities around the globe kept time based on local solar observations, which led to considerable differences and inevitable complications in coordination. The creation of GMT offered a standardised time framework, thus introducing an element of unity in global timekeeping.
The GMT framework, set at the Prime Meridian (0° longitude), was based on the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich. The term 'GMT' gradually became synonymous with the time zone UTC+00:00 and formed the legal basis for civil time in the UK.
However, GMT, as originally calculated, was not always precisely in sync with solar time, leading to potential discrepancies up to 0.9 seconds. Consequently, GMT is not typically used for functions requiring high precision. The advent of atomic clocks, which provide a much more stable time base, further emphasised the limitations of GMT as a precise time standard.
GMT has left an indelible mark on the UK's heritage and beyond. As Britain grew into a formidable maritime nation, GMT became an essential navigational tool for British mariners. They used chronometers set to GMT to calculate their longitude from the Greenwich meridian, effectively using GMT as a reference point for global navigation.
This practice was formalised during the International Meridian Conference in 1884, which declared Greenwich as the longitude zero degrees. GMT consequently became a standard time used globally, regardless of location. Most of the world's time zones were established with GMT as a reference, using it as the basis for defining the number of hours "ahead of GMT" or "behind GMT".
GMT's impact extended to terrestrial transport as well. In 1847, the Railway Clearing House in Great Britain adopted GMT, leading to its wider acceptance across various railway companies. This led to the term "railway time," signifying the common standard used across the rail network. Despite some legal contention, by 1880, GMT was legally recognised as the official time throughout the island of Great Britain.
GMT's influence on society, transport, and communications has played a significant role in shaping the modern world. Its use is deeply woven into British culture and is frequently referenced by many UK institutions, including the BBC World Service, the Royal Navy, and the Met Office.
GMT was eventually replaced by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on 1 January 1972 as the international civil time standard. Although UTC is often colloquially interchanged with GMT, it is important to note that the two are technically different. UTC, maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks worldwide, provides a more precise and stable time base.
Even the prime meridian of Greenwich underwent changes. The meridian's location was previously defined by "the centre of the transit instrument at the Observatory at Greenwich". However, it is now a statistical solution from observations of all time-determination stations, which the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) uses to coordinate the world's time signals.
Despite the official switch to UTC, GMT continues to hold a significant place in the global consciousness. In the UK, the term GMT is often used during the winter months, while the term British Summer Time (BST) or UTC+01:00 is used during the daylight saving period.
The GMT terminology is also utilised in the broadcasting world. The BBC World Service, for instance, uses the term "Greenwich Mean Time" consistently throughout the year due to its broad global audience across multiple time zones.
Various countries still define their local time by reference to GMT. Certain countries, including the UK, even legislate Greenwich Mean Time as their standard time, demonstrating its continued influence and the enduring legacy of this British contribution to global timekeeping.
In conclusion, Greenwich Mean Time represents a significant part of Britain's historical and cultural heritage. Its introduction standardised global timekeeping, revolutionising navigation, transportation, and communication. Although it has been technically superseded by UTC, GMT remains a prevalent term in everyday language, a testament to its enduring legacy and Britain's significant contribution to our perception of time.
A Pioneering Initiative: The Birth of Greenwich Mean Time
The emergence of GMT can be traced back to 1884 at the Greenwich Observatory in the United Kingdom. Prior to this, towns and cities around the globe kept time based on local solar observations, which led to considerable differences and inevitable complications in coordination. The creation of GMT offered a standardised time framework, thus introducing an element of unity in global timekeeping.
The GMT framework, set at the Prime Meridian (0° longitude), was based on the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich. The term 'GMT' gradually became synonymous with the time zone UTC+00:00 and formed the legal basis for civil time in the UK.
However, GMT, as originally calculated, was not always precisely in sync with solar time, leading to potential discrepancies up to 0.9 seconds. Consequently, GMT is not typically used for functions requiring high precision. The advent of atomic clocks, which provide a much more stable time base, further emphasised the limitations of GMT as a precise time standard.
Contribution to British Heritage and Global Infrastructure
GMT has left an indelible mark on the UK's heritage and beyond. As Britain grew into a formidable maritime nation, GMT became an essential navigational tool for British mariners. They used chronometers set to GMT to calculate their longitude from the Greenwich meridian, effectively using GMT as a reference point for global navigation.
This practice was formalised during the International Meridian Conference in 1884, which declared Greenwich as the longitude zero degrees. GMT consequently became a standard time used globally, regardless of location. Most of the world's time zones were established with GMT as a reference, using it as the basis for defining the number of hours "ahead of GMT" or "behind GMT".
GMT's impact extended to terrestrial transport as well. In 1847, the Railway Clearing House in Great Britain adopted GMT, leading to its wider acceptance across various railway companies. This led to the term "railway time," signifying the common standard used across the rail network. Despite some legal contention, by 1880, GMT was legally recognised as the official time throughout the island of Great Britain.
GMT's influence on society, transport, and communications has played a significant role in shaping the modern world. Its use is deeply woven into British culture and is frequently referenced by many UK institutions, including the BBC World Service, the Royal Navy, and the Met Office.
Evolving with Time: From GMT to UTC
GMT was eventually replaced by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on 1 January 1972 as the international civil time standard. Although UTC is often colloquially interchanged with GMT, it is important to note that the two are technically different. UTC, maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks worldwide, provides a more precise and stable time base.
Even the prime meridian of Greenwich underwent changes. The meridian's location was previously defined by "the centre of the transit instrument at the Observatory at Greenwich". However, it is now a statistical solution from observations of all time-determination stations, which the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) uses to coordinate the world's time signals.
GMT in the Contemporary World
Despite the official switch to UTC, GMT continues to hold a significant place in the global consciousness. In the UK, the term GMT is often used during the winter months, while the term British Summer Time (BST) or UTC+01:00 is used during the daylight saving period.
The GMT terminology is also utilised in the broadcasting world. The BBC World Service, for instance, uses the term "Greenwich Mean Time" consistently throughout the year due to its broad global audience across multiple time zones.
Various countries still define their local time by reference to GMT. Certain countries, including the UK, even legislate Greenwich Mean Time as their standard time, demonstrating its continued influence and the enduring legacy of this British contribution to global timekeeping.
In conclusion, Greenwich Mean Time represents a significant part of Britain's historical and cultural heritage. Its introduction standardised global timekeeping, revolutionising navigation, transportation, and communication. Although it has been technically superseded by UTC, GMT remains a prevalent term in everyday language, a testament to its enduring legacy and Britain's significant contribution to our perception of time.
- Greenwich Mean Timeen.wikipedia.org