British Heritage
Remember, Cherish, Learn.
beta
Science
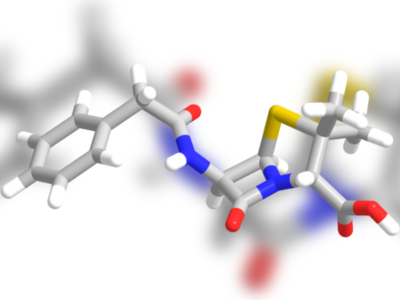
Contribution of Sir Alexander Fleming to British Heritage.
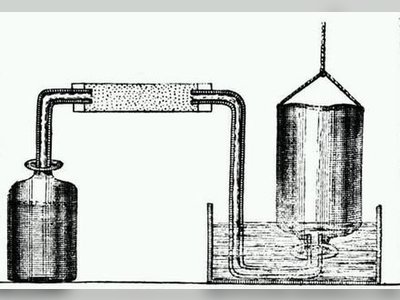
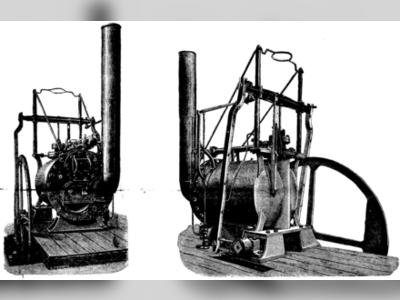
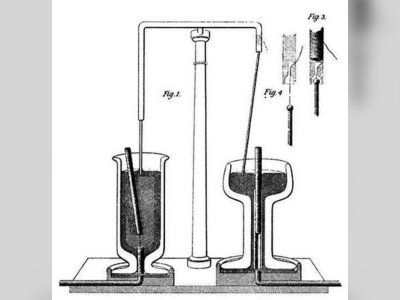
Contribution of Henry Cavendish to British Heritage.
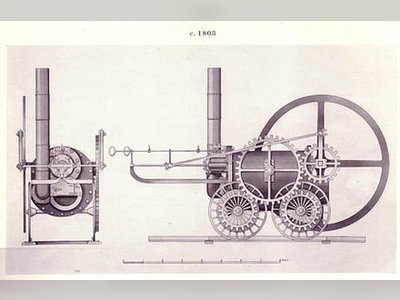
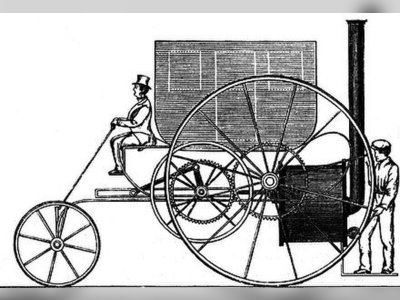
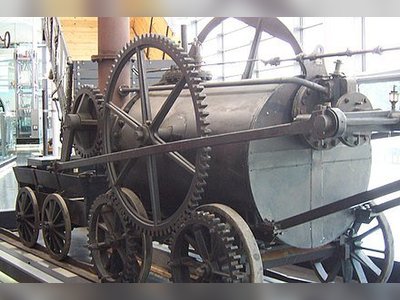
Contribution to British Heritage.
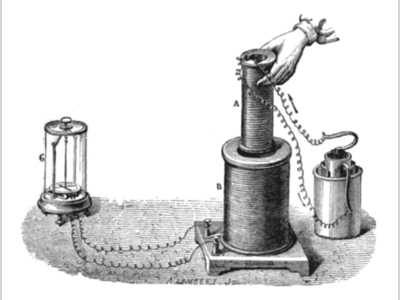
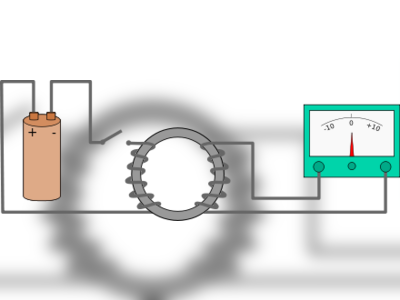
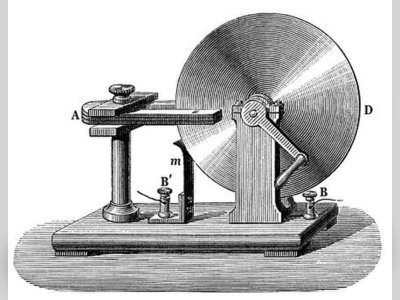
Contribution of Michael Faraday to British Heritage.
Contribution to British Heritage.
Theoretical Physicist: A Pillar of British Heritage.
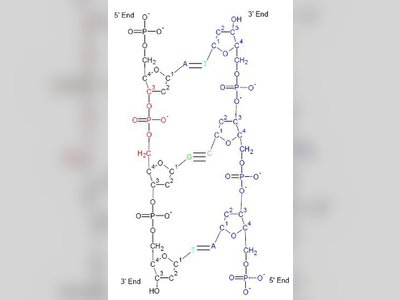
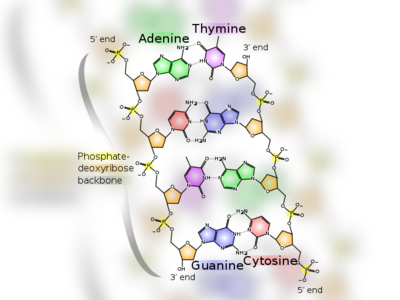
Contribution to British Heritage: Deciphering the DNA Structure.
A Defining Contribution to British Heritage.
Ethical Contributions to British Heritage.
The Legacy of Science Parks in Britain: A Testament to Innovation
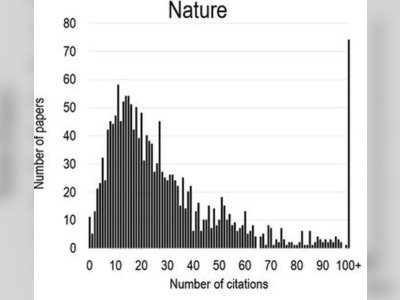
Contribution of Nature Journal to British Heritage.
A Pioneering Jewel of British Heritage.