Philosophers
***TOO LONG***Thomas Paine (1737–1809) was an English-born American political activist, philosopher, political theorist, and revolutionary. He authored Common Sense (1776) and The American Crisis (1776–1783), two of the most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and helpe...
***TOO LONG*** Under his pen name "George Orwell", Eric Arthur Blair (1903 –1950), was an English novelist, essayist, journalist and critic. Best known known for the allegorical Animal Farm (1945) and the dystopian Nineteen Eighty-Four (1949), his work remains influential in popular and politic...
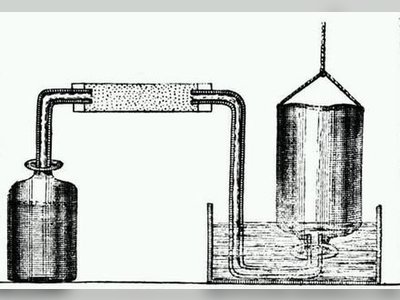
Contribution of Henry Cavendish to British Heritage.
Contribution to British Heritage.
Contribution to British Heritage.
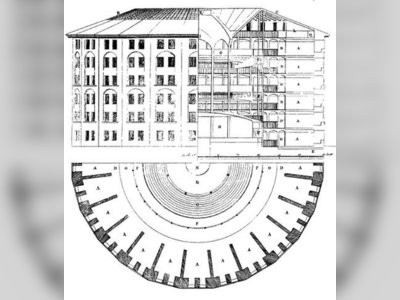
Champion of Social Reform and Utilitarian Philosophy.