James Wolfe
A Hero of British Heritage.
Introduction
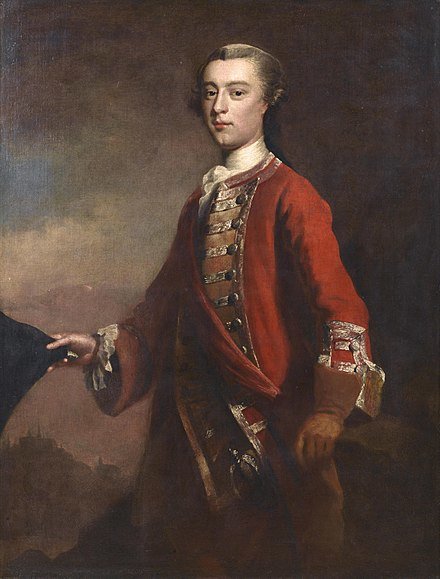
James Wolfe, a renowned British Army officer, left a lasting legacy in British history through his military achievements and victories during the Seven Years' War. Born on 2 January 1727 in Westerham, Kent, Wolfe's illustrious military career was marked by training reforms and successful campaigns, most notably his victory at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham in Quebec. His contributions to British heritage, military leadership, and dedication to duty made him an iconic figure in Britain's history of territorial expansion and victory in the Seven Years' War.
Early Military Career and Training Reforms
James Wolfe's military journey began at a young age when he received his first commission in his father's regiment, the 1st Marine Regiment, at the age of thirteen. He saw extensive service in Europe during the War of the Austrian Succession, distinguishing himself as a young officer. His service in Flanders and his role in suppressing the Jacobite Rebellion in Scotland earned him recognition from his superiors.
Wolfe's dedication and exceptional skills propelled his rapid rise through the ranks. At just 18, he became a brigade major, and by the age of 23, he held the rank of lieutenant-colonel. His abilities as a leader and strategist were further honed during the unsuccessful Rochefort raid in 1757, which led to his appointment as second-in-command in an expedition to capture the Fortress of Louisbourg.
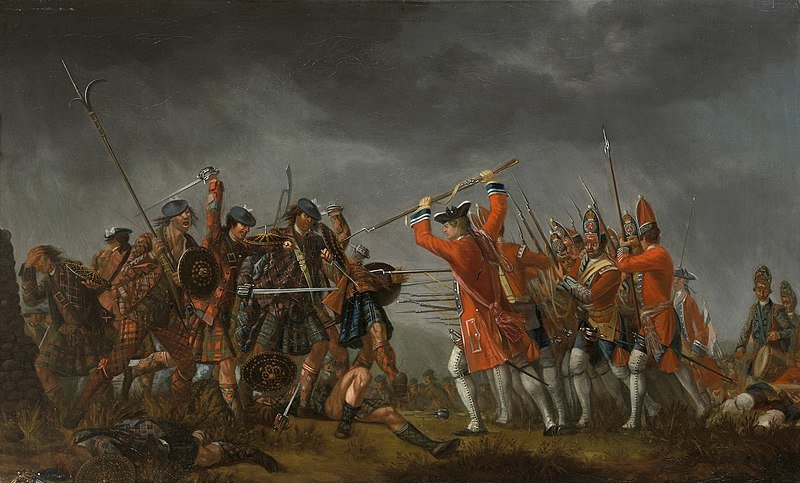
The Battle of the Plains of Abraham and Wolfe's Victory
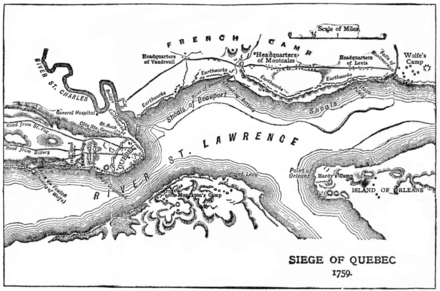
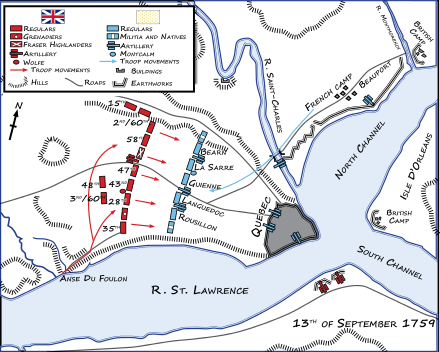
Wolfe's most famous achievement came in 1759 during the Seven Years' War when he led the British forces to victory at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham in Quebec. After a long siege, Wolfe defeated the French forces under the Marquis de Montcalm, resulting in the capture of Quebec City. Tragically, Wolfe was fatally wounded during the height of the battle by three musket balls.
Contribution to British Heritage
James Wolfe's triumph at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham marked a significant moment in British heritage. The capture of Quebec City directly led to the capture of Montreal, ending French control of Canada. This victory secured Britain's dominance in North America and expanded its territorial holdings. As a result of this conquest, Wolfe earned the posthumous titles of "The Hero of Quebec," "The Conqueror of Quebec," and "The Conqueror of Canada," becoming an enduring symbol of Britain's success in the Seven Years' War.
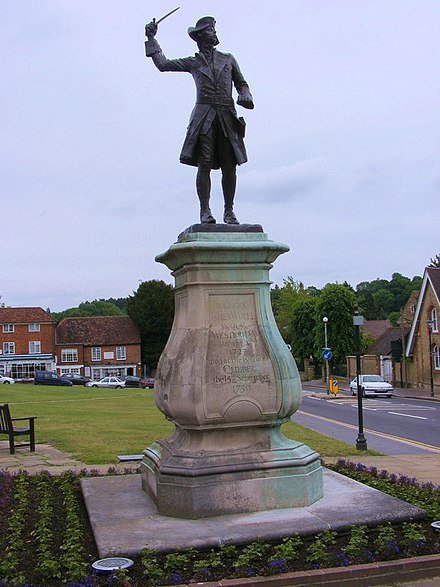
Legacy and Commemorations
Wolfe's contributions to British heritage are commemorated in various ways. The famous painting "The Death of General Wolfe" by Benjamin West immortalized his heroism and sacrifice on the battlefield. Several statues and memorials, including those at Westminster Abbey and Greenwich, honor his memory.
Many places in Canada bear Wolfe's name, attesting to his significance in the nation's history. The Wolfe Landing National Historic Site of Canada in Nova Scotia marks the site of his successful landing during the Siege of Louisbourg. Additionally, the Wolfe Island, named by Governor John Graves Simcoe, and several other landmarks in Canada, celebrate his legacy.
Conclusion
James Wolfe's life and military achievements left a profound impact on British heritage and its history. His victories in the Seven Years' War, particularly the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, secured British dominance in North America and expanded its territorial holdings. His dedication to duty, training reforms, and exemplary leadership made him an iconic figure in British military history, forever remembered as "The Hero of Quebec" and "The Conqueror of Canada." Today, his name and legacy continue to be honored through various monuments, memorials, and landmarks in both Britain and Canada, reminding us of the valor and sacrifices of this great military leader.
- James Wolfeen.wikipedia.org