British Heritage
Remember, Cherish, Learn.
beta
Michael Faraday - The Electric Motor
The Electric Motor and Contributions to British Heritage.
Introduction
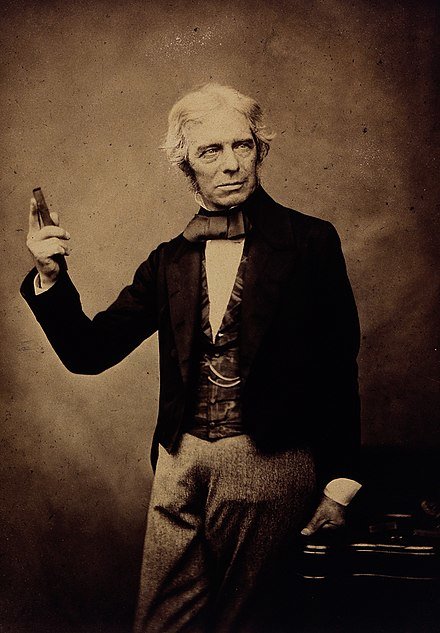
Michael Faraday, a pioneering English scientist, left an indelible mark on the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His groundbreaking discoveries and inventions revolutionized the understanding of electricity and magnetism, paving the way for countless technological advancements. Among his numerous contributions, one of the most significant was the development of the electric motor, a revolutionary invention that transformed modern society. Faraday's work not only shaped the scientific landscape of his time but also laid the foundation for the technological progress that continues to define British heritage and the global scientific community.
Faraday's Early Life and Education
Michael Faraday was born on September 22, 1791, in Newington Butts, Surrey, which is now part of the London Borough of Southwark. His family's modest background did not provide him with formal education, but his insatiable curiosity and self-education would ultimately lead him to become one of the most influential scientists in history. At the age of 14, Faraday began an apprenticeship with George Riebau, a bookbinder and bookseller, during which he devoured various books, including those on science and electricity.
The Path to Electromagnetism
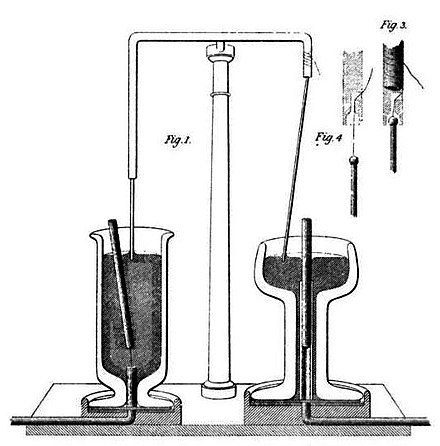
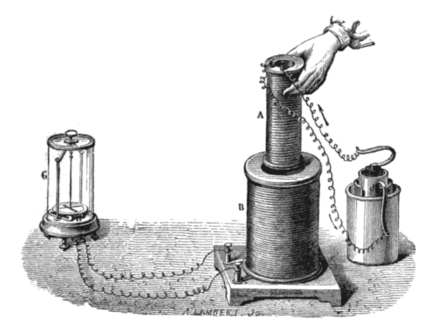
Faraday's journey to electromagnetism began in 1821 when he conducted a pivotal experiment involving a magnet and a pool of mercury. By passing an electric current through a wire wrapped around the magnet, he observed the rotation of the magnet in the mercury, establishing the principle of electromagnetic rotation. This discovery laid the groundwork for the development of the electric motor, a device that would later revolutionize industrial processes and transportation.
Electromagnetic Induction and Dynamism
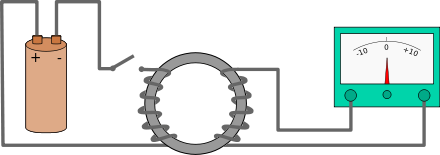
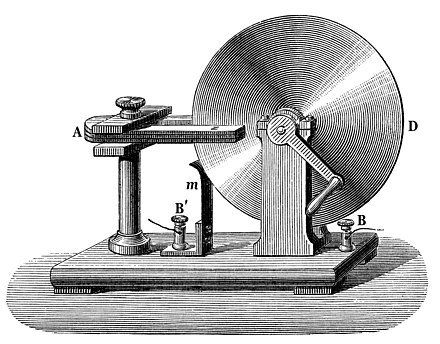
In 1831, Faraday made another groundbreaking discovery: electromagnetic induction. By moving a magnet near a conductor, he demonstrated that an electric current could be induced in the wire. This fundamental principle laid the foundation for the generation of electricity and led to the invention of the electric dynamo, a device that converted mechanical energy into electrical energy. Faraday's work on electromagnetism and dynamism marked a turning point in the practical application of electricity and spurred the development of electrical technologies that continue to shape the world today.
Faraday's Legacy and Contributions to British Heritage
Faraday's contributions to British heritage and the global scientific community are immeasurable. His pioneering work on electromagnetism and the electric motor not only paved the way for technological advancements but also laid the groundwork for modern power generation and distribution systems. Without Faraday's foundational research, the inventions of other renowned figures like Nikola Tesla and William Sturgeon would not have been possible.
Furthermore, Faraday's influence extended beyond scientific research. As a devout Christian, he saw no conflict between his faith and his scientific pursuits. Faraday viewed his scientific inquiries as a way to explore the wonders of God's creation, and his deep convictions inspired generations of scientists to embrace both science and faith.
Honors and Recognition
Throughout his lifetime, Faraday received numerous honors and accolades for his remarkable achievements. In 1824, he was elected a member of the prestigious Royal Society, and in 1833, he became the first Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution of Great Britain, a position he held for life. His dedication to public engagement and science education led him to deliver a series of Christmas lectures for young people, which remain a tradition to this day.
Even after his passing on August 25, 1867, Faraday's legacy endured. Streets, buildings, and awards around the world bear his name, paying tribute to the immense impact of his work. He was ranked 22nd on the BBC's list of the 100 Greatest Britons, a testament to his lasting influence and contributions to British heritage.
Conclusion
Michael Faraday's genius and relentless pursuit of knowledge transformed the world of science and technology. His work on electromagnetism and the electric motor revolutionized modern society and shaped the foundations of electrical engineering. As a devout man of faith, he also demonstrated that science and religion can coexist harmoniously. Faraday's legacy continues to inspire scientists and engineers to push the boundaries of human knowledge, leaving an enduring mark on British heritage and the global scientific community. His name will forever be etched in the annals of history as one of the greatest scientific discoverers of all time.
- Michael Faradayen.wikipedia.org